ISO 26262 Automotive Functional Safety
Understanding ISO 26262:2018 Automotive Safety Standard
ISO 26262:2018, Road Vehicles – Functional Safety, is a crucial risk-based safety standard for all automotive electronic and electrical (E/E) safety-related systems. Derived from the renowned Functional Safety standard, IEC 61508, this international standard is applicable throughout the life-cycle of safety-related systems involving electronic and/or electrical components.
The latest version was published in late 2018, replacing the earlier ISO 26262:2011 and previous drafts (DIS & FDIS) for all systems initiated after 2018. This comprehensive standard not only applies to series production passenger cars but also extends its guidance to E/E systems used in trucks, buses, trailers, semi-trailers, and motorcycles (excluding mopeds).
ASIL and Safety Classification
ISO 26262 specifies four Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL A to D), with ASIL D representing the highest safety level. The classification is based on the likelihood of potential events and their potential severity. Understanding these ASIL levels is vital for risk assessment and implementation of appropriate safety measures.
The Importance of ISO 26262:2018 for Legal Compliance
In an era of increasing fitness-for-purpose litigation, ISO 26262:2018 serves as a crucial technical standard adopted by legal experts to interpret laws. In Europe, the General Product Safety Directive 2001/95/EC (GPSD) is the relevant law in question. It places the responsibility on product creators to develop safety-critical products in accordance with ‘State-of-the-Art’ development principles. In this context, ‘State-of-the-Art’ refers to commonly accepted best practices, which now find embodiment in ISO 26262:2018. Companies that neglect industry practices may lose the « State-of-the-Art » legal defense against litigation.

ISO 26262:2018 is the definitive safety standard for road vehicles, encompassing various aspects of automotive functional safety. Familiarity with ASIL levels and legal implications is essential for ensuring compliance and mitigating risks in the development of E/E systems.
By adhering to ISO 26262:2018, automotive companies can prioritize safety and meet the requirements of modern product safety directives.
Ensuring ISO 26262 Compliance with Software Testing Tools and Techniques
When it comes to guaranteeing the functional safety of automotive electronic and electrical (E/E) safety-related systems, compliance with ISO 26262 is of utmost importance. Rigorous testing throughout the development life cycle is essential to identify potential hazards and mitigate risks.
- Unit Testing Implementation: To achieve ISO 26262 compliance, the implementation of unit testing is crucial. Utilizing software testing tools, such as static code analysis tools, helps in identifying coding errors, ensuring that each unit of code functions correctly and meets specified safety requirements. This ensures that software components are free from critical defects.
- Functional Testing Techniques: Employing functional testing techniques is vital for ISO 26262 compliance. Dynamic testing tools can execute the software and validate its behavior against the expected functionality. This includes testing boundary conditions, exceptional scenarios, and safety mechanisms, ensuring that the software behaves as intended during regular and fault conditions.
- Structural Testing Techniques: For comprehensive compliance, adopting structural testing techniques, like code coverage analysis tools, assists in assessing how much of the software’s code has been tested. High code coverage instills confidence that the software has been thoroughly tested, enhancing its reliability and reducing potential safety risks.
- Fault Injection Testing: Simulating potential faults through fault injection testing allows engineers to evaluate the system’s response to failures and assess safety mechanisms’ effectiveness. This testing helps identify weaknesses in the software design and enhances its resilience against potential safety hazards.
- Verification and Validation: Achieving ISO 26262 compliance also involves performing verification and validation using testing tools and techniques. This produces the necessary evidence required by ISO 26262, including test reports, test results, traceability matrices, and documentation that showcases rigorous testing to meet safety standards.
QA Systems enable organizations to expedite ISO 26262 compliance through automated static analysis and software testing tools. Our tools streamline the compliance process, ensuring the safety and reliability of automotive electronic and electrical systems.
STATIC ANALYSIS
Static Analysis for ISO 26262 compliance
Part 6 of ISO 26262 addresses product development at the software level, providing tables defining the necessary methods to achieve compliance with the standard.
Static Analysis is particularly valuable in meeting clause 8, « Unit design and implementation, » within part 6 of the standard. QA-MISRA ensures the software adheres to coding standards specified in section 5.4.7 and required by section 8.4.3.d.
For more information on Static Analysis, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Our “QA-MISRA Safety Manual” summarizes the ISO 26262 static analysis recommendations by ASIL and how QA-MISRA and Astrée support these requirements.
Start a free trial of QA-MISRA to evaluate your code against MISRA, AUTOSAR, CERT C/C++, CWE and other coding standards to ensure automated compliance with ISO 26262.

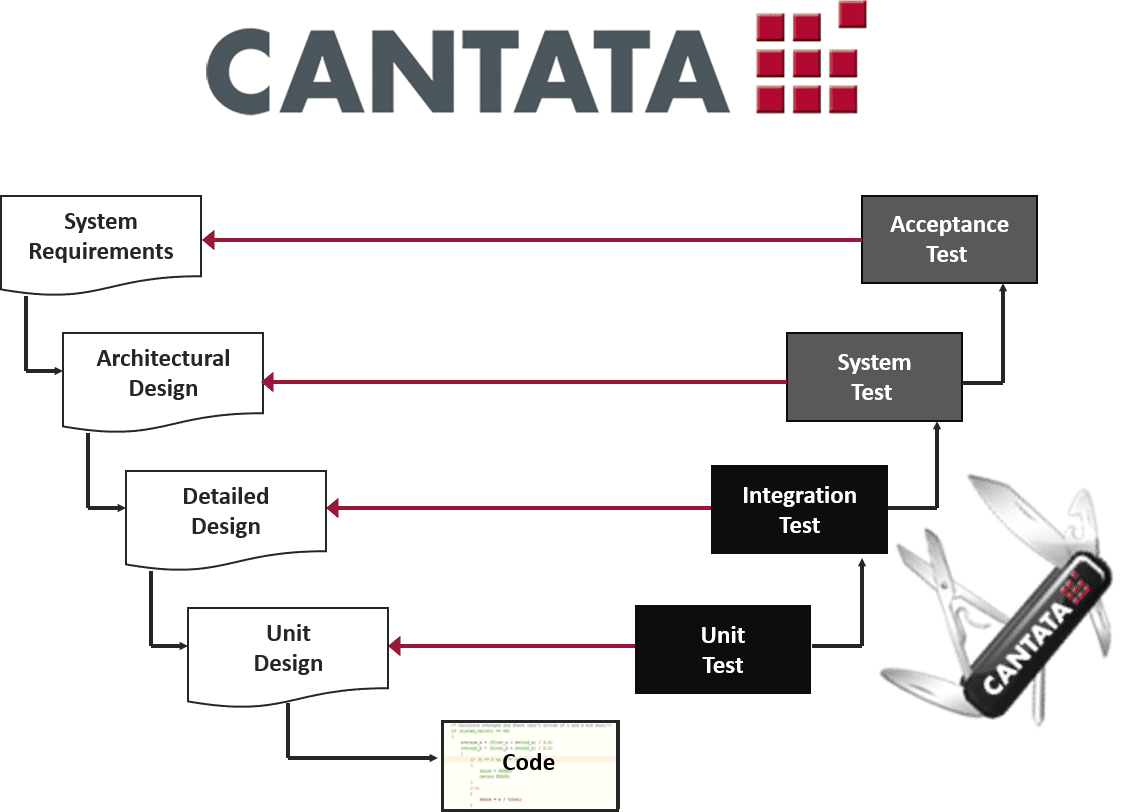
Dynamic testing for ISO 26262 compliance
Section 6 of ISO 26262 recommends unit and integration testing. The Cantata testing tool enables developers to automate their unit and integration testing and verify ISO 26262 compliant code on host native and embedded target platforms.
Cantata helps accelerate compliance with the standard’s dynamic testing requirements by automating:
Please contact us for more information on Cantata for ISO 26262.
The ISO 26262 dynamic testing recommendations by ASIL and how these are supported by Cantata are summarised in our White Paper “Cantata Standard Briefing ISO 26262”
Start a free trial & get a complete copy of Cantata to evaluate using your code.
Tool Certification & Qualification
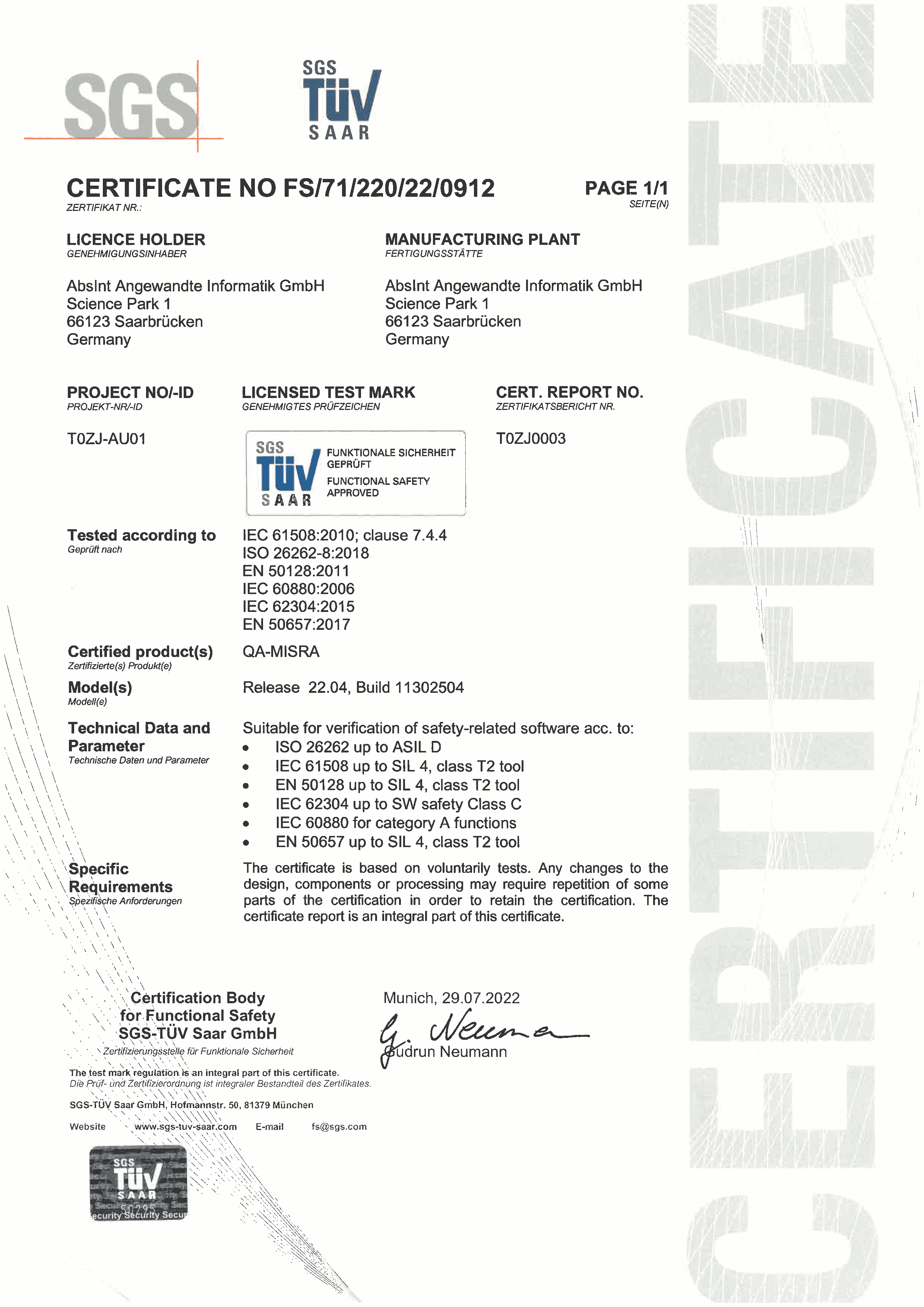
ISO 26262, Part 8 section 11, defines the qualification process for software tools. Accordingly, our dynamic testing tool, Cantata, has been classified and certified by SGS-TÜV GmbH, an independent third-party certification body for functional safety, accredited by Deutsche Akkreditierungsstelle GmbH (DAkkS). Cantata has achieved a Tool Confidence Level (TCL) 1 classification, making it suitable for developing safety-related software according to ISO 26262:2018, up to Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) D.
Regarding our static analysis tool, QA-MISRA, its Tool Qualification Support Kit (QSK) automatically executes a comprehensive tool qualification verification test suite on the installed tool configuration and generates necessary reports for ISO 26262 tool qualification.
These ISO 26262 tool kits are designed to facilitate our customers’ path to certification. They include everything necessary to18px demonstrate that Cantata and QA-MISRA instill the required confidence in using software tools, aligning with ISO 26262 recommendations. Additionally, the kits provide comprehensive and detailed guidance on leveraging these tools to comply with the necessary software verification activities of ISO 26262.
Please contact us for more information about these tool kit.